Standard & Smart 3S BMS wiring tutorial
Take a 3S12P 18650 battery pack as an example.
Be careful not to insert the BMS when soldering the cable.
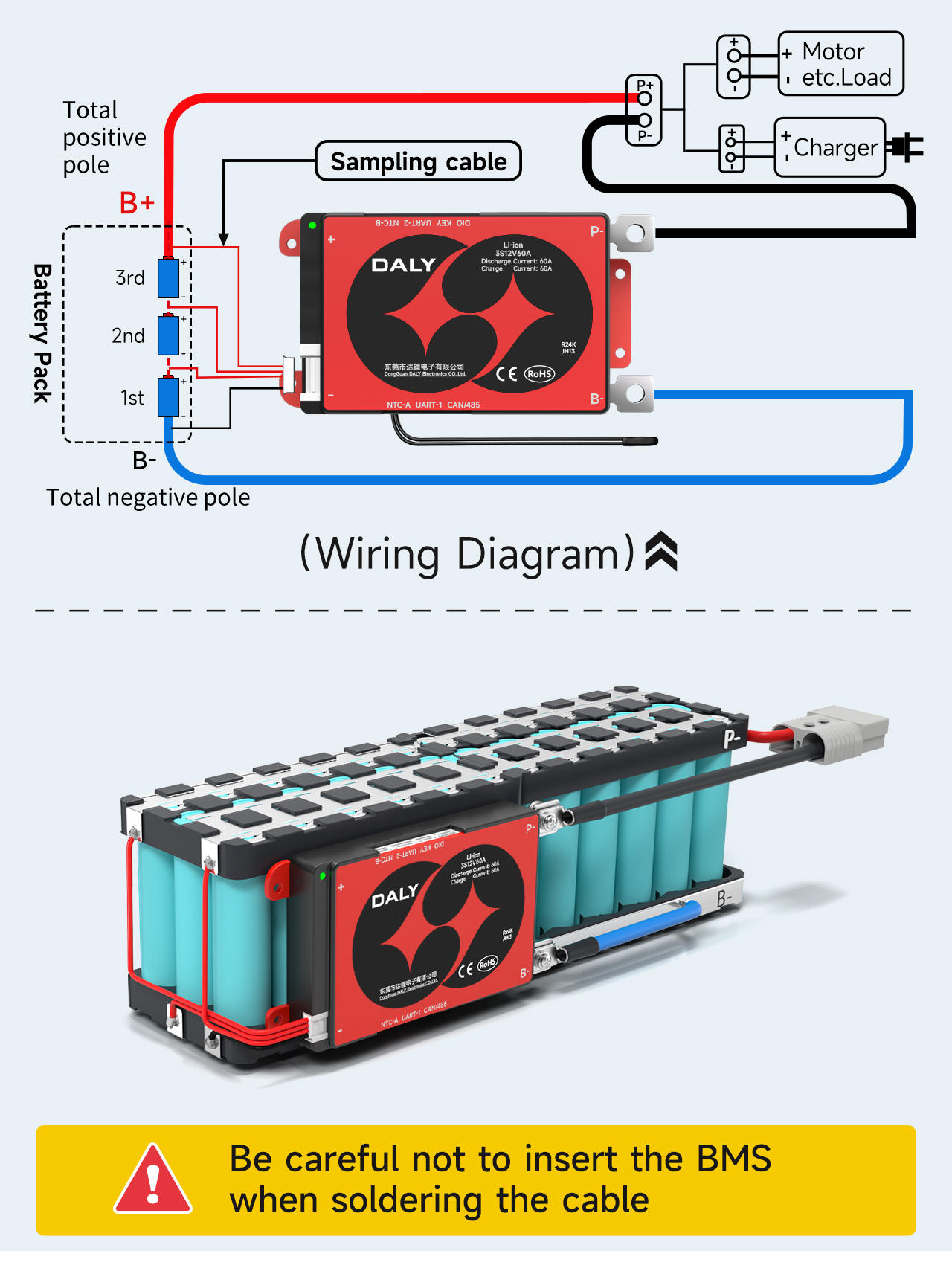
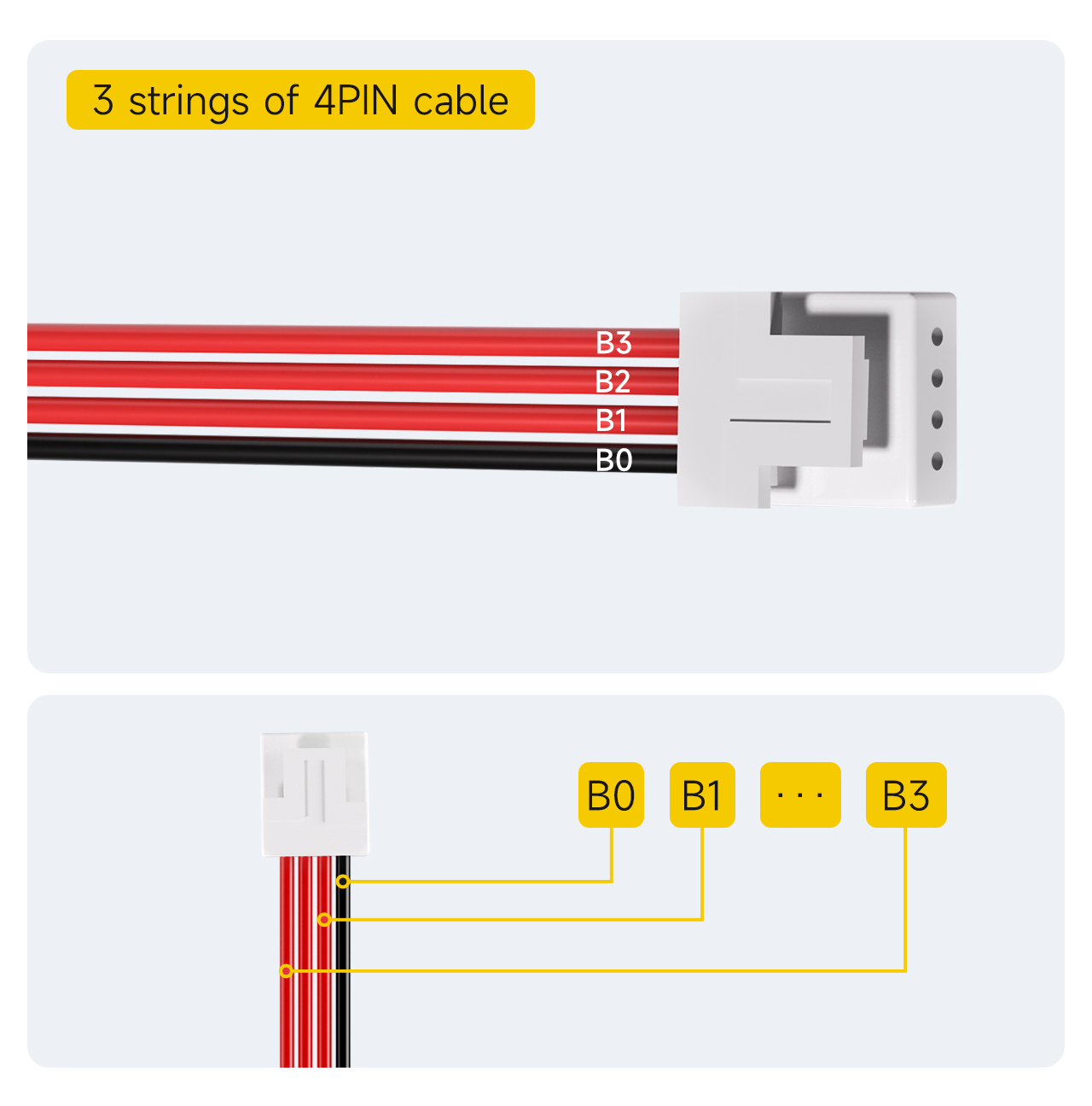
Ⅰ. Mark the order of sampling lines
3S BMS with 4PIN
Note: The default sampling cable for 3-string BMS configuration is 4PIN.
1. Mark the black cable as B0.
2. The first red cable next to the black cable is marked as B1.
... (and so on, marked sequentially)
4. Until the last red cable, marked as B3.
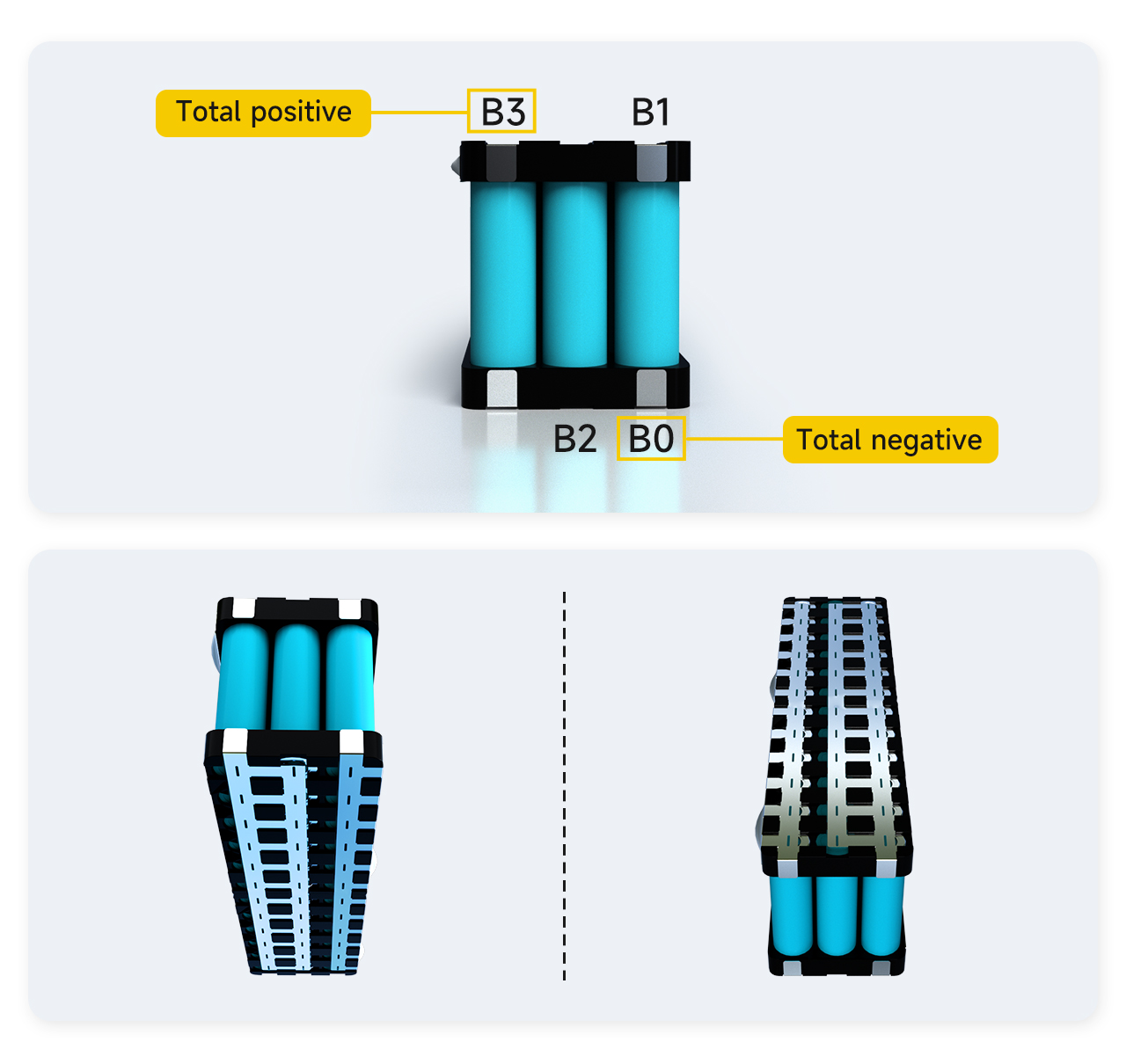
Ⅱ. Mark the order of battery welding points
Find the position of the corresponding welding point of the cable, first mark the position of the corresponding point on the battery.
1. The total negative pole of the battery pack is marked as B0.
2. The connection between the positive pole of the first string of batteries and the negative pole of the second string of batteries is marked as B1.
3. The connection between the positive pole of the second string of batteries and the negative pole of the third string of batteries is marked as B2.
4. The positive electrode of the 3th battery string is marked as B3.
Note: Because the battery pack has a total of 3 strings, B3 is also the total positive pole of the battery pack. If B3 is not the total positive stage of the battery pack, it proves that the order of marking is wrong, and it must be checked and marked again.
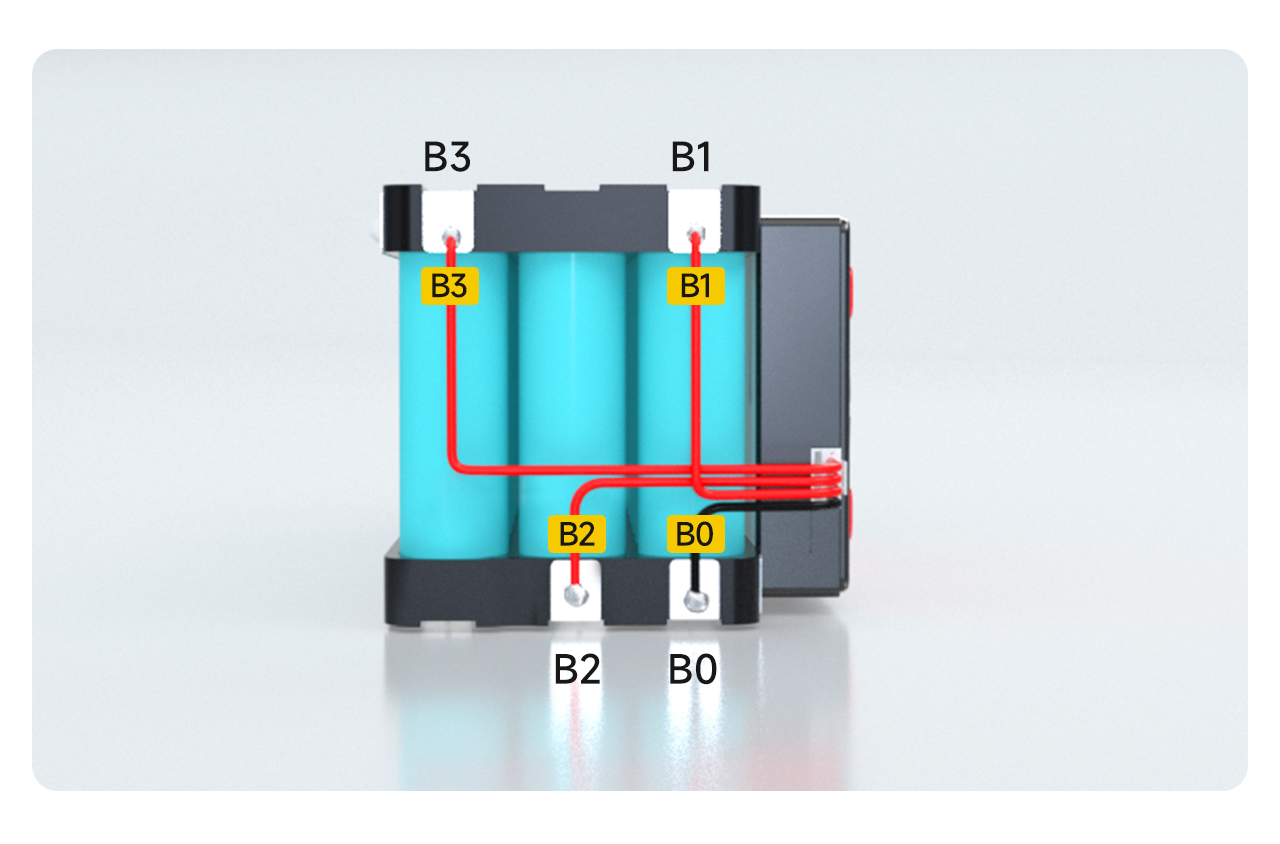
Ⅲ. Soldering and wiring
1. The B0 of the cable is soldered to the B0 position of the battery.
2. The cable B1 is soldered to the B1 position of the battery.
3. The cable B2 is soldered to the B2 position of the battery.
4. The cable B3 is soldered to the B3 position of the battery.
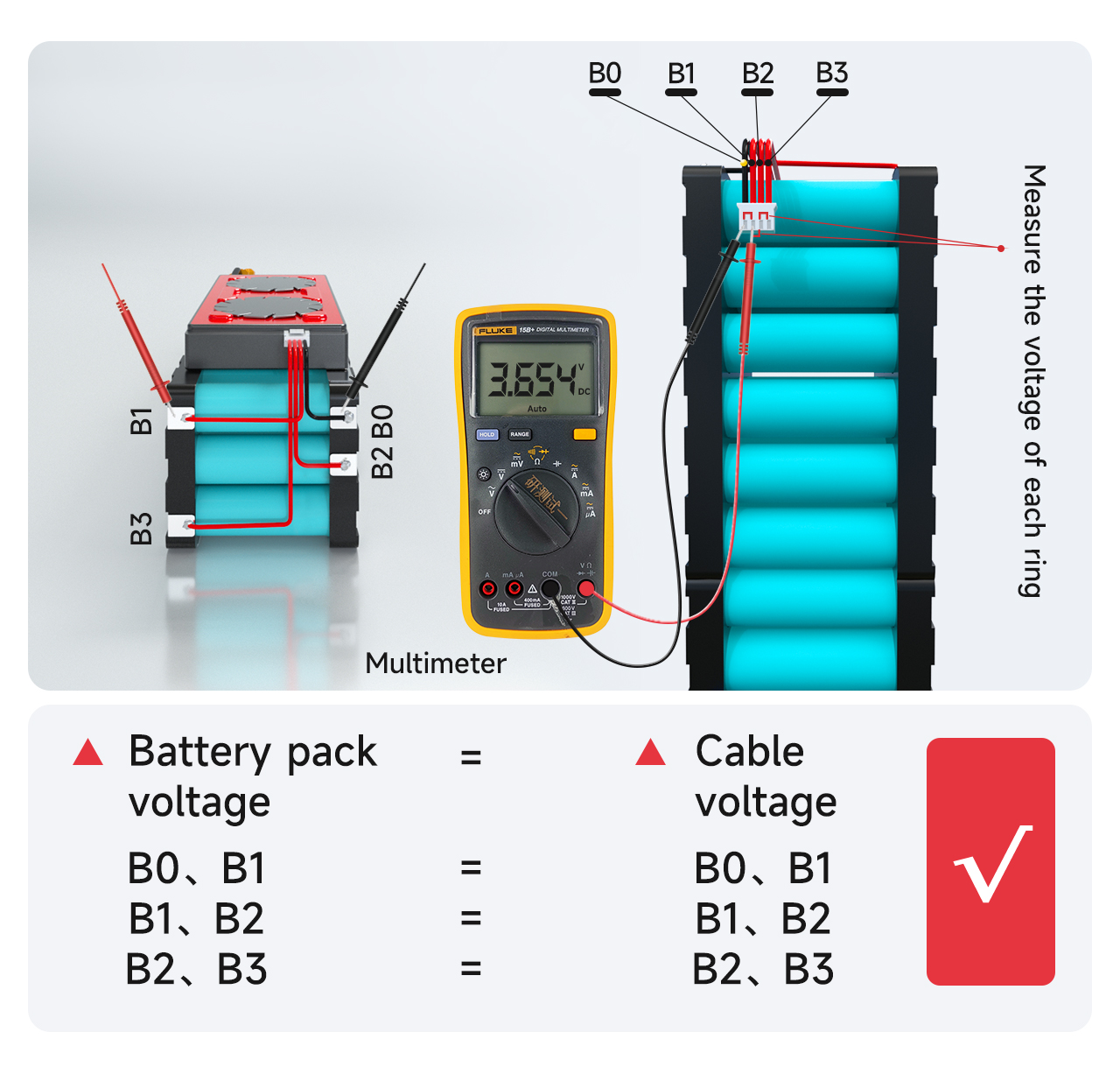
Ⅳ. Voltage Detection
Measure the voltage between adjacent cables with a multimeter to confirm that the correct voltage is collected by the cables.
Measure whether the voltage of the cable B0 to B1 is equal to the voltage of the battery pack B0 to B1. If it is equal, it proves that the voltage collection is correct. If not, it proves that the collection line is weakly welded, and the cable needs to be re-welded. By analogy, measure whether the voltages of other strings are collected correctly.
2. The voltage difference of each string should not exceed 1V. If it exceeds 1V, it means that there is a problem with the wiring, and you need to repeat the previous step for detection.
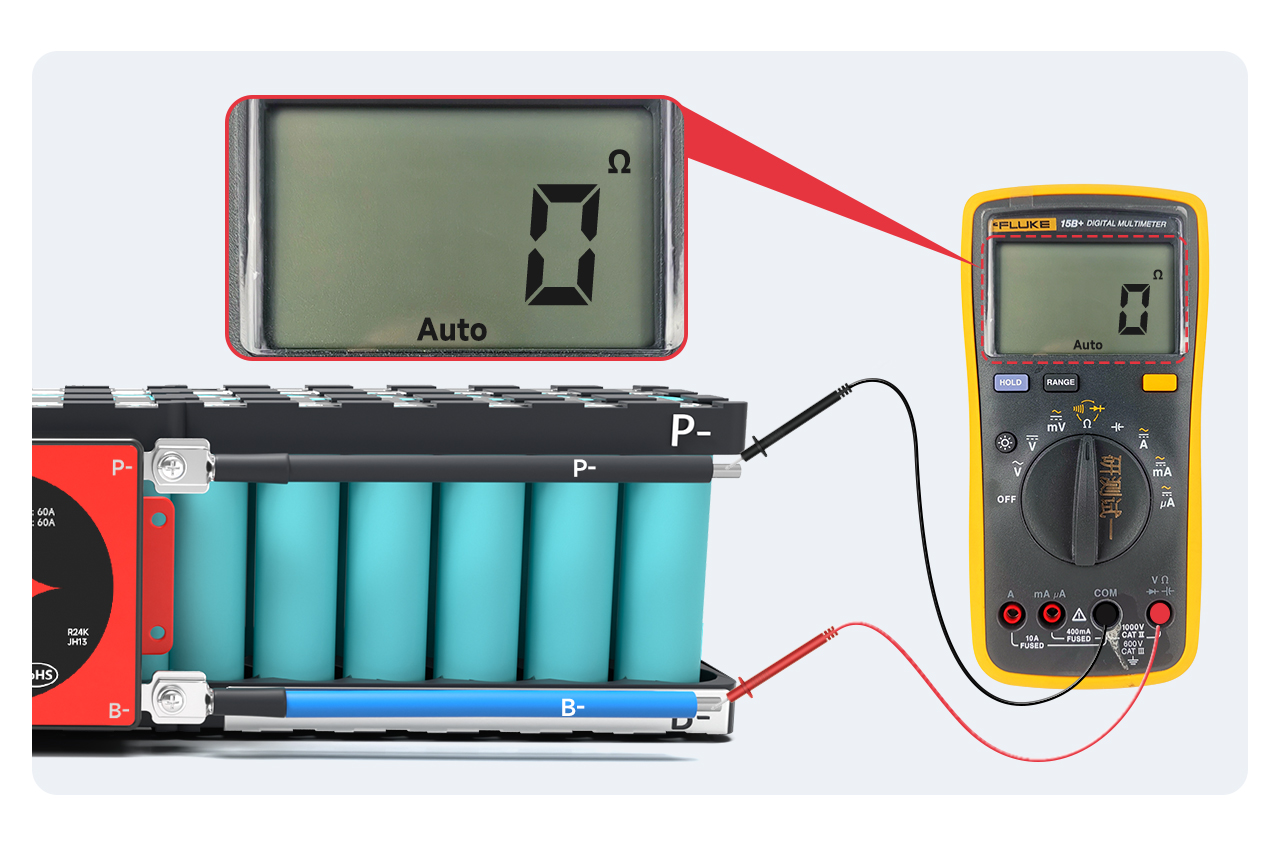
Ⅴ. BMS quality detection
! Always make sure the correct voltage is detected before plugging in the BMS!
Adjust the multimeter to the internal resistance level and measure the internal resistance between B- and P-. If the internal resistance is connected, it proves that the BMS is good.
Note: You can judge the conduction by looking at the internal resistance value. The internal resistance value is 0Ω, which means conduction. Due to the error of the multimeter, generally, less than 10mΩ means conduction; you can also adjust the multimeter to the buzzer. A beeping sound can be heard.

Note:
1. The BMS with a soft switch needs to pay attention to the conduction of the switch when the switch is closed.
2. If the BMS is not conducting, please stop the next step and contact the sales staff for processing.
Ⅵ. Connect the output line
After ensuring that the BMS is normal, solder the blue B- wire on the BMS to the total negative B- of the battery pack. The P-line on the BMS is soldered to the negative pole of charge and discharge.
After welding, check whether the voltage of the over BMS is consistent with the battery voltage.
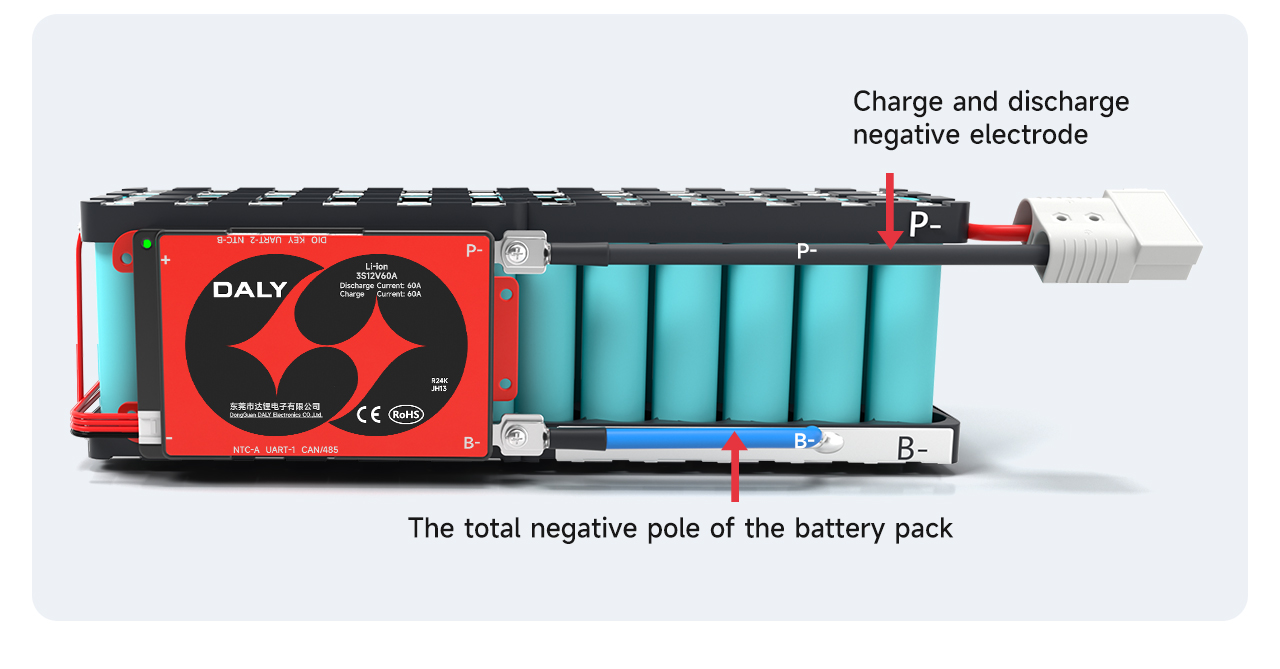

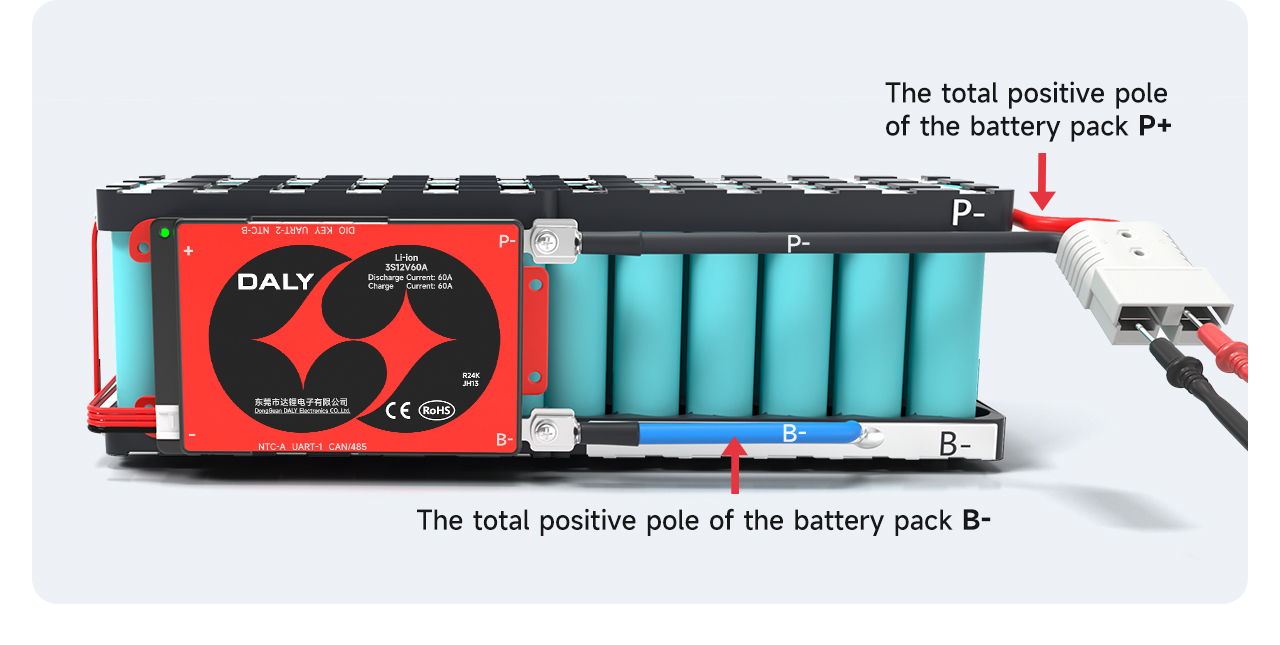
Note: The charging port and discharge port of the split BMS are separated, and the extra C-line (usually indicated by yellow) needs to be connected to the negative pole of the charger; the P-line is connected to the negative pole of the discharge.
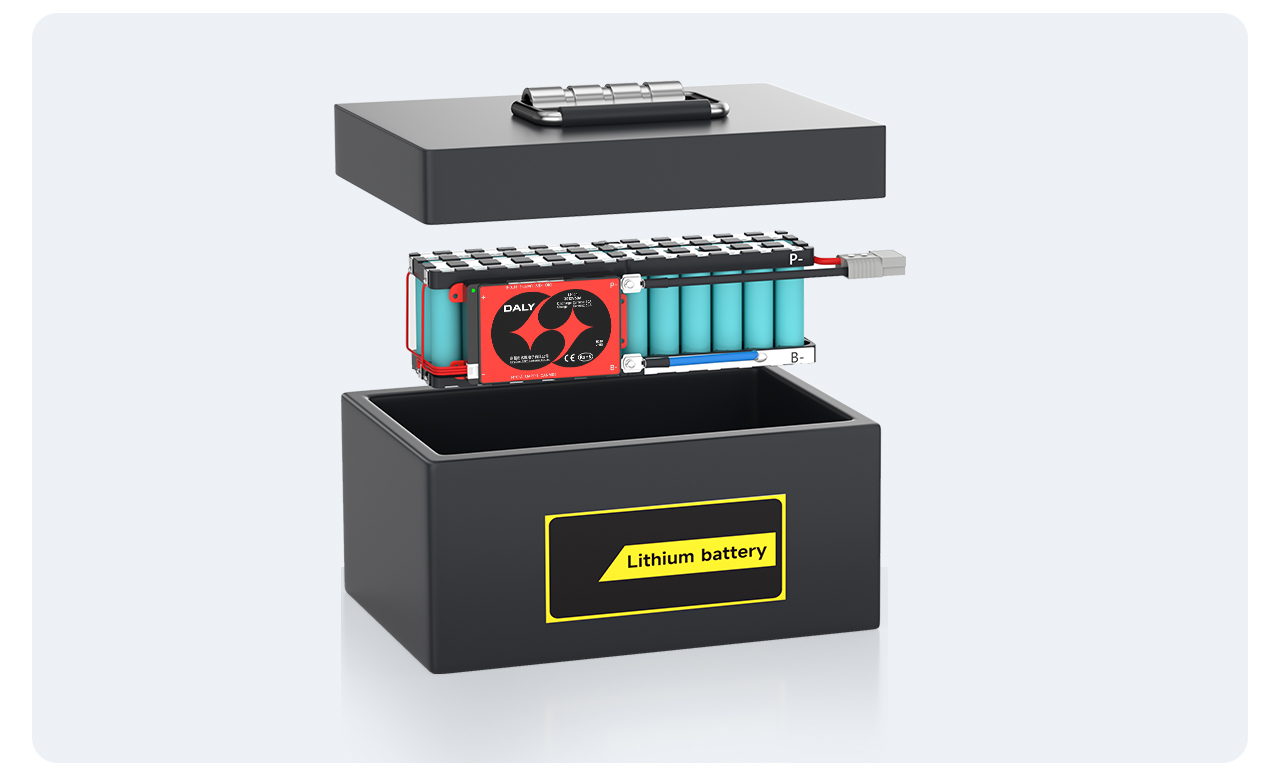
Finally, place the battery pack inside the battery box, and a finished battery pack is assembled.






